Medial Epicondylitis (Golfers Elbow) and Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
Golfers & Tennis Elbow
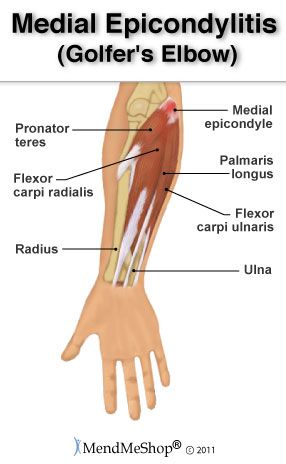
Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis are known as Tennis Elbow or Golfer’s Elbow and are an inflammation of the tendons of the arm.
These injuries tend to be quite common and mostly occur because of overuse. These tendons are bands of tough tissue that connect the muscles of the arm to bone. Despite the names of Golfer and Tennis elbow these injuries occur quite often in people who do not play these sports, rather an overuse or repetitive use that may occur because of work or activities that inflame these tendons. Tennis elbow or Lateral Epicondylitis is the most common of the two and although it can happen to anyone, it is more common in people over the age of 40.
For tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis repetitive motion like grabbing a racquet , during a swing can strain muscles and put stress onto tendons they attach to. These constant movements cause microscopic tears in the tissue.
Causes of Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Tennis
- Racquetball
- Squash
- Fencing
- Weight lifting
- Carpentry
- Typing
- Painting
- Raking
- Knitting
Signs And Symptoms Of Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Pain and tenderness in bone outside of elbow. The pain can radiate into the upper or lower arm, but mostly lower arm
- Most pain will occur when lifting or making a fist or gripping an object
- Open a door and shaking hands
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) Signs And Symptoms
- Pain and tenderness in inner side of elbow
- Stiffness when making a fist
- Weakness in hands and wrist
- Can experience numbness and tingling sensation that can radiate into the ring and little finger
The symptoms may appear gradually or suddenly with pain. Activities usually aggravate the condition.
Treatment Of Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) And Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
- Initially reducing pain inflammation and swelling
- Strengthening weak muscles and stretching contracted muscles
- Physiotherapy, Massage Therapy and Acupuncture can all be effective in treating these conditions